Usability

Source: Google images
Hundreds of good features included in a product will go unused or unnoticed if the user interface designed is complex or confusing to use. Hence, usability plays a vital role in Software Product Development. Usability is defined as the ease with which an application can be used by a user to achieve the specified set of goals in a particular environment (context of use).
Let us understand the Usability Metrics that can be used to measure the usability of a Software Product.
Usability Metrics
International Standards Organisation (ISO) recommends that a software product usability can be measured using the following metrics:

Let us understand the Usability Requirements of a software product to satisfy these metrics.
Usability Requirements
According to International Standards Organisation, software product usability requirements should include the following:

Icons source: Google images
After understanding the usability requirements, the next important step is the design of the User Interface.
User Interface Design (UID)
User Interface Design or UI Design is the design of screens using which the user will interact with the software to achieve specified set of goals. According to Human Factors International (HFI), there are four important dimensions which needs to be applied to any screen design and are:
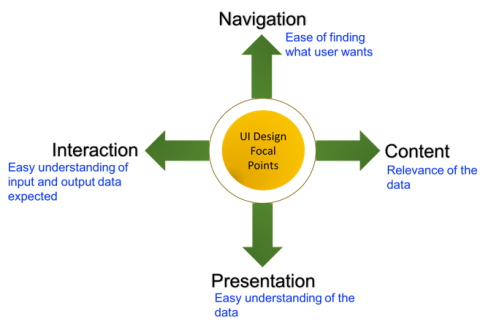
User interface design should be centered around the user of the product and this is called as User Centered Design discussed in the next section.
User Centered Design (UCD) & User Experience Design (UXD)
User Centered Design (UCD) is an approach where the UI is designed from the perspective of the user who will be using the product. HFI defines three important profiles to be considered for UCD:

Icons source: Google images
User stories, task flows, surveys, interviews, focus groups are the different methods which helps in collection of data for these profiles.
User Experience Design (UXD) is an approach for creating UCD. UXD is the process of conducting research with the intended users of the product through surveys, interviews, focus groups and activities which will allow users to express their emotions and motivations about their task(s). This in turn will help to create user centered design in a way that users will experience the use of the product as acceptable and satisfying.
Apart from usability, it is also important that the product meets the internationalisation requirements to reach global audience. Next section defines Internationalisation, Localisation, Globalisation requirements.
Internationalisation, Localisation, Globalisation
Understanding of the differences with respect to business practices, acceptable vs offensive and formats, are important considerations for building a product to address international audience. To satisfy this, it is imminent that the product meets the internationalisation requirements as shown in the figure below:

Note: Incase of support for Asian languages, the product also needs to support multi-byte character set for Chinese, Korean, Japanese languages.
Examples of Internalisation:
- United States follows ‘mm/dd/yyyy’ format whereas Germany follows ‘dd.mm.yyyy’ format
- ‘Program’ in US English and ‘Programme’ in UK English,
- Arabic language is written/read from right to left and English from left to right.
- Color ‘red’ denotes danger in US and in China it denotes happiness.
- Italian, French and German are the languages used in Switzerland. In this case, the software has to support all these three languages. There can also be scenario where German is the spoken language but writing is done in English.
- Another example,

Source: Human Factors International
Good Principles of User Interface Design for any Software Product
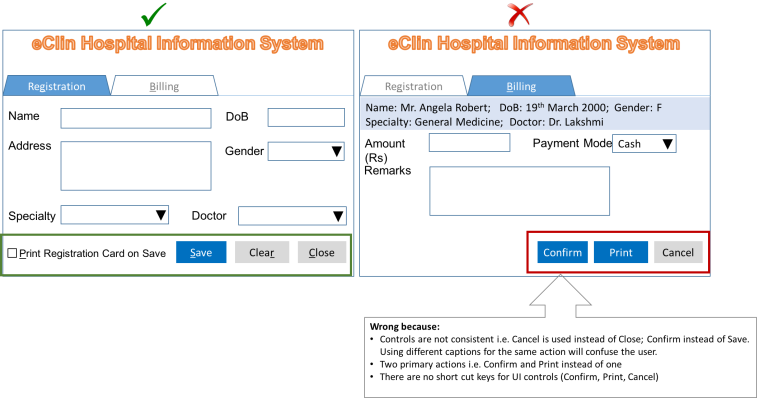
- Keep UI elements consistent, one primary action per screen and shortcut keys for user actions.
2. Avoid information overflow on the interface
3. Build intelligence to the product

4. Include worklist and workflows for scheduled tasks that need user’s attention/approval

Icon source: Google images
5. Group similar tasks and display the goal of the User Interface
6. Finally, ensure that UI elements fits well when viewed on a tab or smartphone

Conclusion
Incorporating usability requirements along with the four important focal points of user interface design makes the product more intuitive and less complicated to use. It is paramount that the software is designed keeping the user in mind i.e. his/her task profiles, environment profiles and location profiles. Product also needs to accommodate internationalisation requirements if it is intended for the global audience. A good design of the software product is critical for the growth of the business. Hence, it is essential that the organization invests time and effort in creating a good design of their software product.

Great post! Clarifies the fundamentals in a lucid way.
LikeLike
Thanks so much Vinay!!!
LikeLike